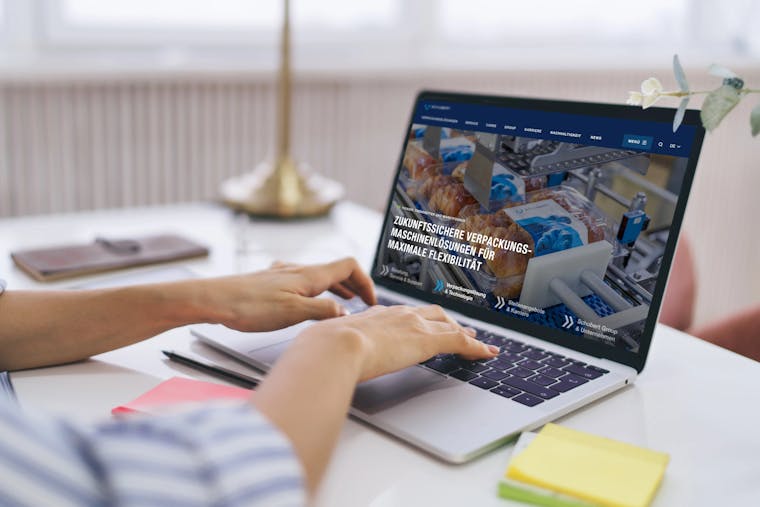
B2B website agency for sales- and marketing-driven websites
In B2B, the role of the website has fundamentally changed. In an environment shaped by AI, fragmented customer journeys, and international competition, websites are no longer just communication channels or classic IT projects. At the same time, many companies hesitate precisely at this point: the effort appears high, the business impact difficult to quantify, and the risk of organizational friction significant.
Yet the reality is clearly shifting. As demand, reach, and leads can no longer be generated reliably through personal sales contacts alone, the website moves back to the center. Not as a monolithic relaunch, but as a scalable platform that addresses markets, captures search intent, and systematically supports sales – across borders.
In practice, this ambition rarely fails because of technology. More often, it is shaped by early strategic decisions: responsibilities, decision-making logic, governance models, and tool requirements often influence website projects more strongly than the actual objectives.
As a strategic digital agency for B2B, we develop, design, and deliver websites from exactly this perspective. We take full operational responsibility – from concept and design to technology, development, operation, and continuous improvement. Our goal is to build and run websites that create sustained impact through the interaction of content, online marketing, and lead processes. Not as a one-off project, but as an active marketing and sales system in continuous operation.
Clarifying the role of your website
Finding the next meaningful step – together
If you are considering what role your website should play in the future for visibility, market development, or lead processes, a short conversation can be valuable.
Unbinding, structured, and tailored to your specific starting point.



Why clarity determines impact
The role of the website in B2B companies today
Making Decisions Before Implementation
Approach to Website Projects
Understand users. Create impact
From Complexity to Clarity
Organization Beats Tool Debates
Making the Right Technology Decisions
Technology only creates impact through real use
From Stack to Implementation


Freedom for Marketing and Markets
Implementation That Enables Momentum
Actively Evolving Websites
Impact Happens in Operations
Enabling Growth Systematically
Website Visibility, Markets, and Leads
When the effort is truly worth it
Using the Website Intentionally
Clarify the role of your website
If you are considering what function your website should take on in the future—
for visibility, markets, or lead processes—
it can be valuable to take a joint look at your current situation and the available options.



FAQs
Frequently asked questions
about B2B Website Agency
A website project is worth it when the requirements for visibility, markets, or lead processes change. This is often the case during international expansion, new service or product areas, shifting target audiences, or when marketing and sales need stronger digital support.
If it’s only about minor updates or maintenance, a fundamental rebuild is usually not necessary.No. In many cases, a full relaunch is neither necessary nor sensible. Existing structures can often be developed step by step: content is reprioritized, specific sections are added, or the technical foundation is modernized gradually. What matters most is not the size of the project, but clarity about the desired impact.
We don’t primarily treat websites as design or IT projects, but as active systems within marketing and sales. That’s why our work starts with positioning the website within the organization—and doesn’t end with go-live. Strategy, implementation, and ongoing operation are aligned so the website delivers impact in everyday use.
Internal teams are a key success factor. Website projects work best when marketing, IT, content, and—where relevant—sales are involved early and have clear roles. We help define responsibilities and decision paths in a way that enables collaboration without adding unnecessary complexity.
International websites bring special requirements for structure, governance, and operations. Local markets need flexibility, while central teams need consistency and control. We build website structures that enable both: central guardrails and local freedom. Content, access rights, and future development are considered from the very beginning.
SEO, content, and performance don’t work alongside the website—they work through it. That’s why we include these aspects in concept, structure, and operations, rather than treating them as isolated services. The goal is a website that can be found, provides relevant content, and supports demand generation systematically.
Very important. Only continuous analytics shows which content is being used, where leads are created, and how markets evolve. These insights form the basis for targeted development. We don’t see optimization as constant tweaking, but as a continuous learning process based on real usage.
That depends heavily on goals, scope, and the starting point. Smaller improvements can often be implemented within a few weeks, while more complex initiatives take longer. More important than a fixed timeline is clear prioritization: what should deliver impact first, and what can follow later?